MELIA
Melia
L., Sp. Pl. ed.1: 384. 1753; Gen. Pl. 5: 182. 1754; Boiss., Fl. Or. 1: 954; 1867; Brandis, Ind. Trees, 140. 1911; T. Cooke, Fl. Bomb. Pres. 2: 205. 1902; Hiern in Hook. f., Fl. Brit. India 2: 543. 1875; Kashyap, Fl. Lahore 62: 1936; Peng & Mabberley, Fl. China @ eFloras.org 11: 130; Fl. Pak. @ eFloras.org
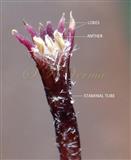
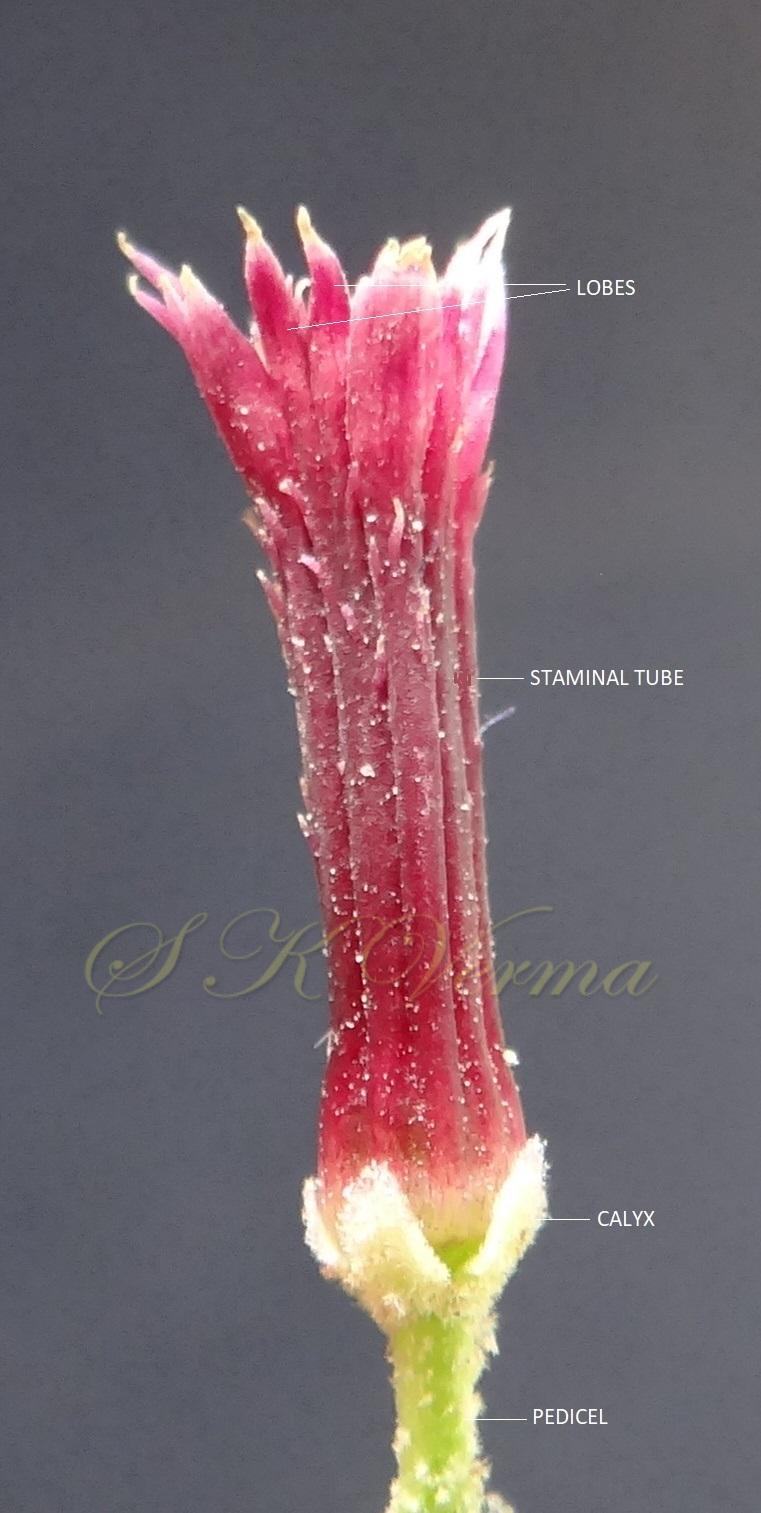
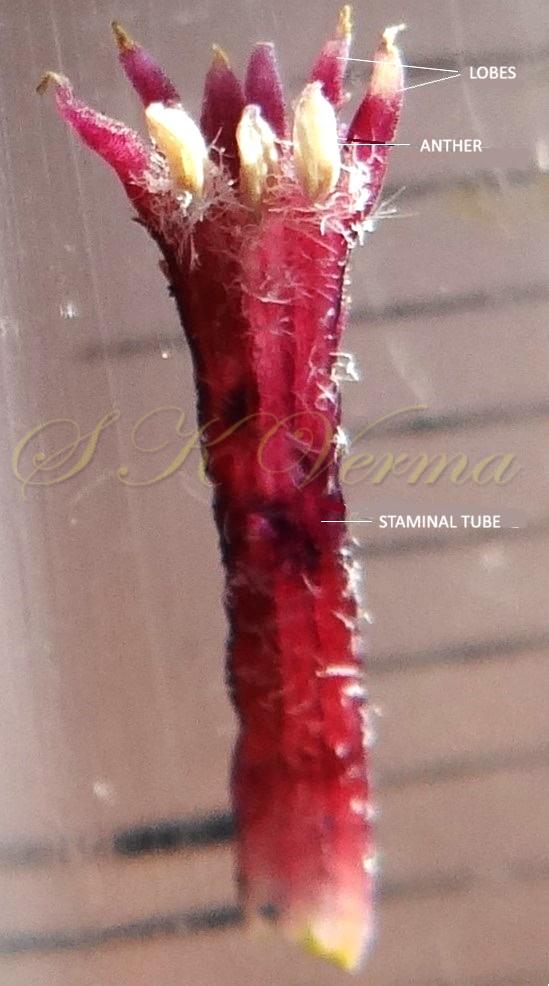
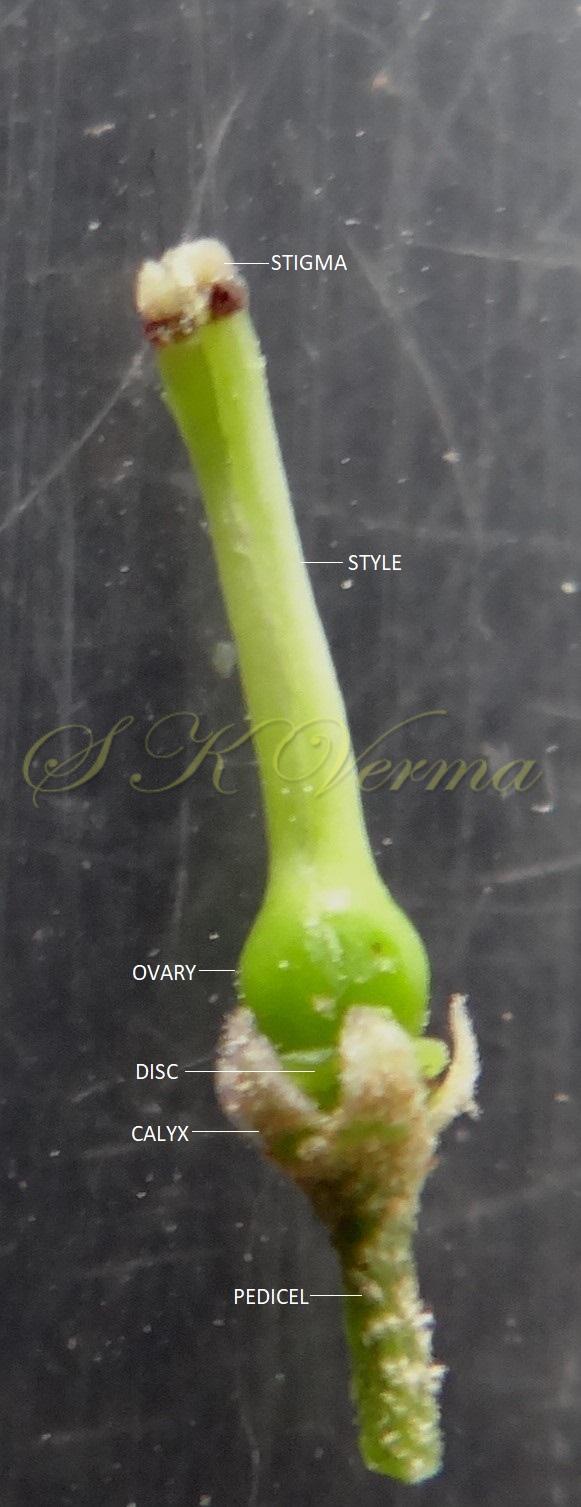
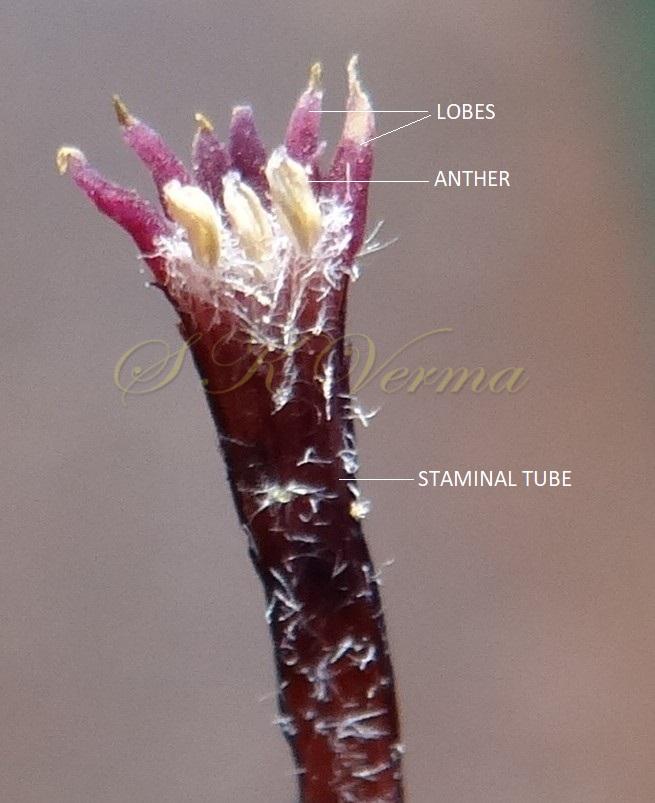
Trees, usually deciduous. Younger parts usually covered with stellate trichomes. Branchlets with obvious leaf scars and lenticels. Leaves alternate, 2(-3)- pinnate; leaflets with petiolules; leaflet blades with margin usually serrate or dentate, sometimes entire. Flowers small, bisexual, actinomorphic, hypogynous, in axillary thyrses or panicles, much branched consisting of several dichasia. Calyx 5- or 6-parted or -lobed. Petals free, white or purple, linear-spatulate, expanding. Stamens 10-12, monoadelphous; staminal tube cylindric with 10-12 ribs, mouth expanding, apex margin 10-12-lobed; anthers 10-13, inserted between staminal tube lobes, included or partly exserted. Disc annular. Ovary subglobose, 3-6-locular, with 2 superposed ovules per locule; stigma capitate. Fruit a drupe, subfleshy; stone bony. Seeds endospermic.
3 species
Melia azedarach
Melia azedarach
L., Sp. Pl. ed.1: 384. 1753; Gen. Pl. 5: 182. 1754; Brandis, Ind. Trees, 140. 1911; Bamber, Fl. Pun. 42. 1916; Bennett in Hajra et al., Fl. India 4: 494. 1997; Cooke, Fl. Bomb. Pres. 2: 205. 1902; Hiern in Hook. f., Fl. Brit. India 2: 543. 1875; Kashyap, Fl. Lahore 62: 1936; Parker, For. Fl. Punj. ed. 1: 72. 1918 (Reprint 1973); Peng & Mabberley, Fl. China @ eFloras.org 11: 130; Fl. Pak. @ eFloras.org; M. orientalis M. Roem., Fam. Nat. Syn. Monogr. 1: 95. 1846.
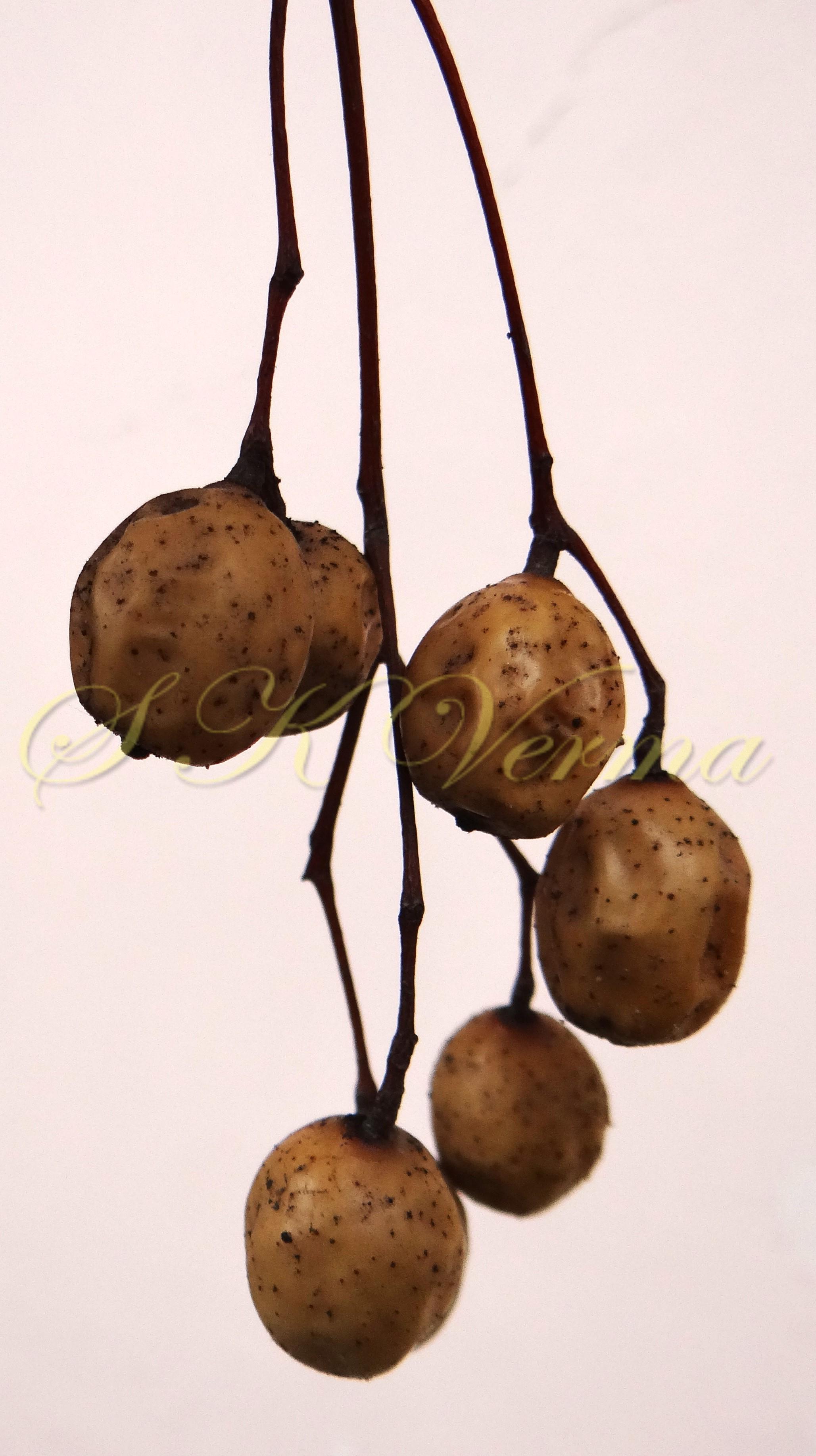
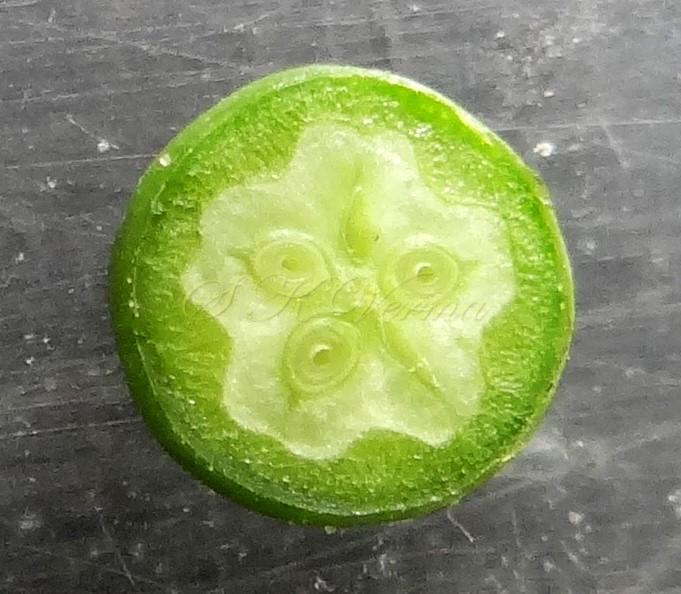
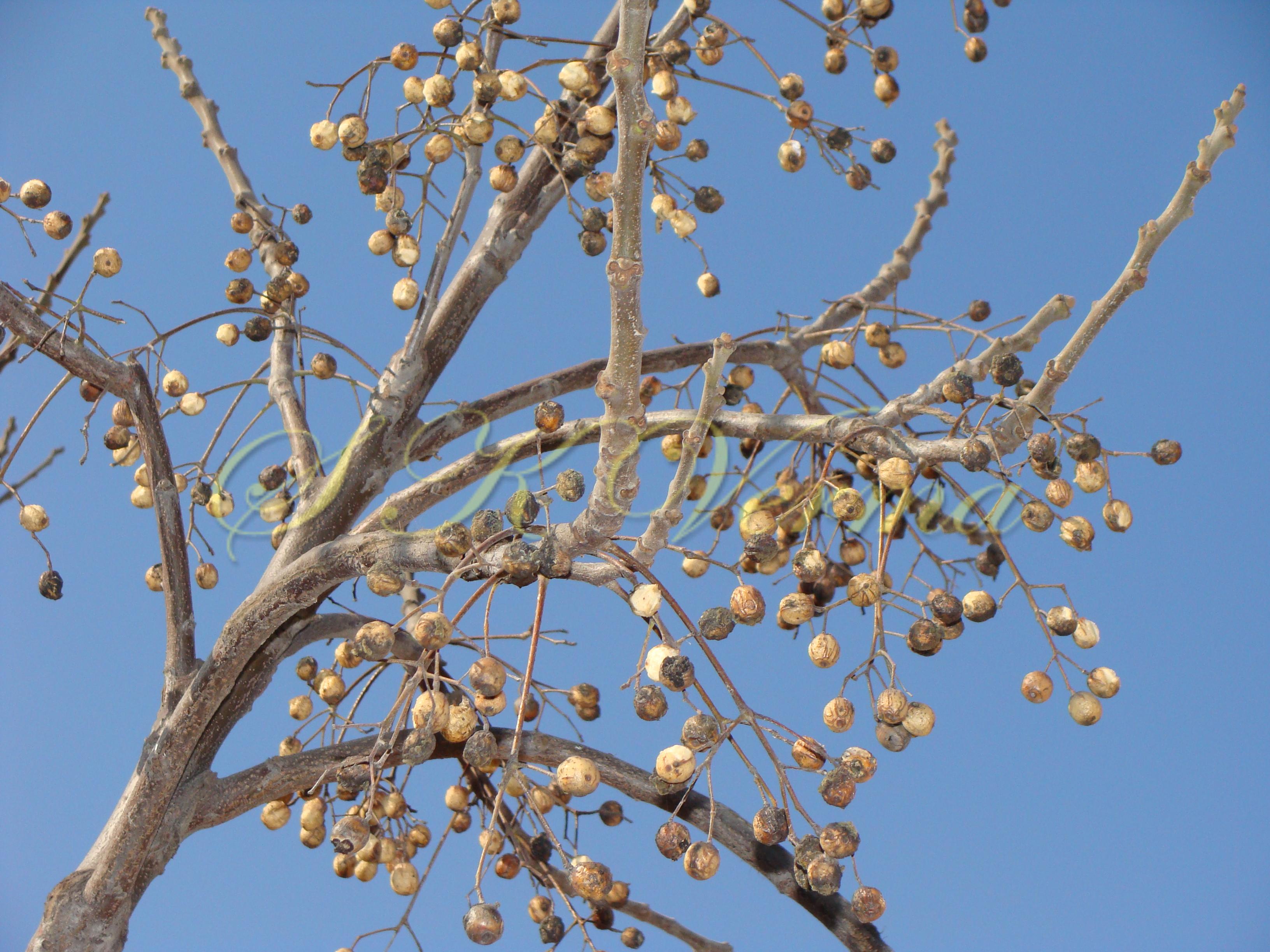
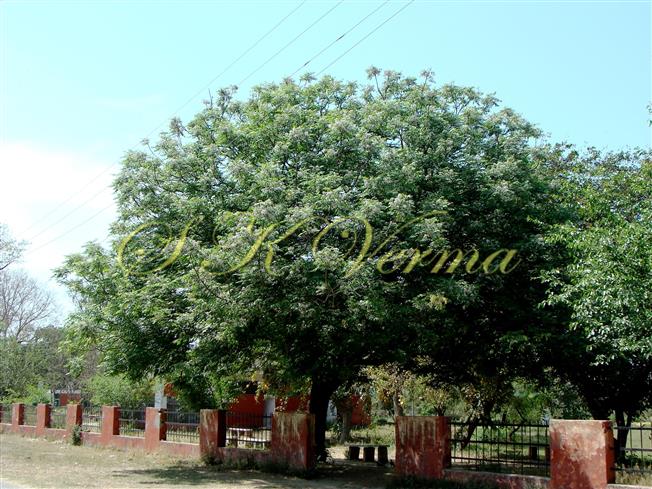
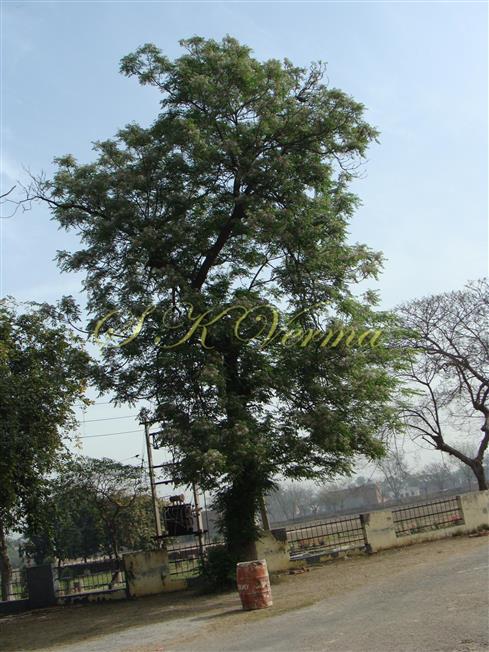
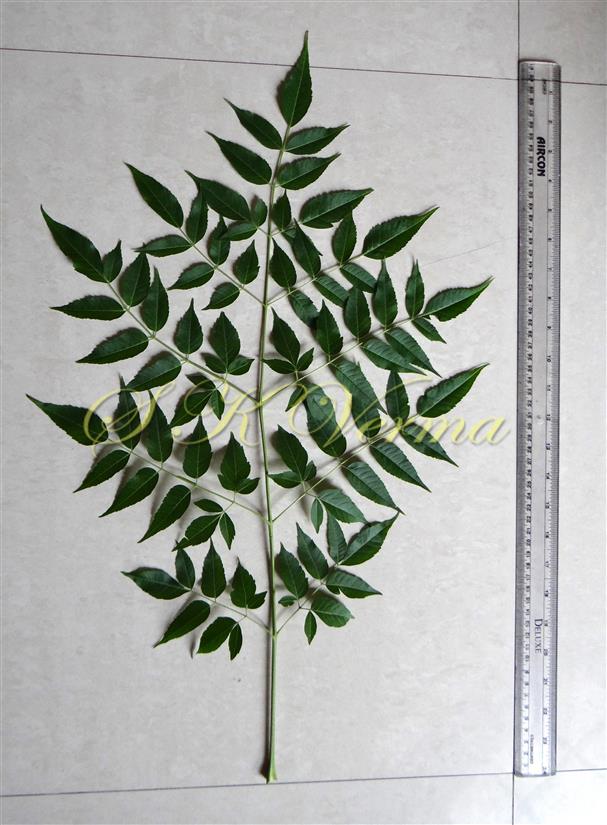
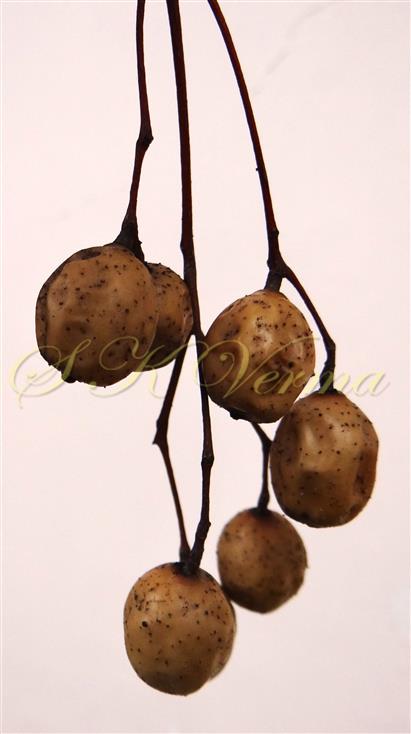
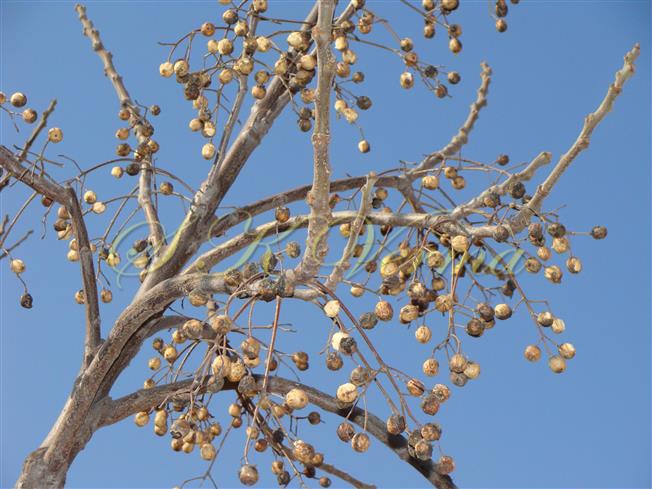
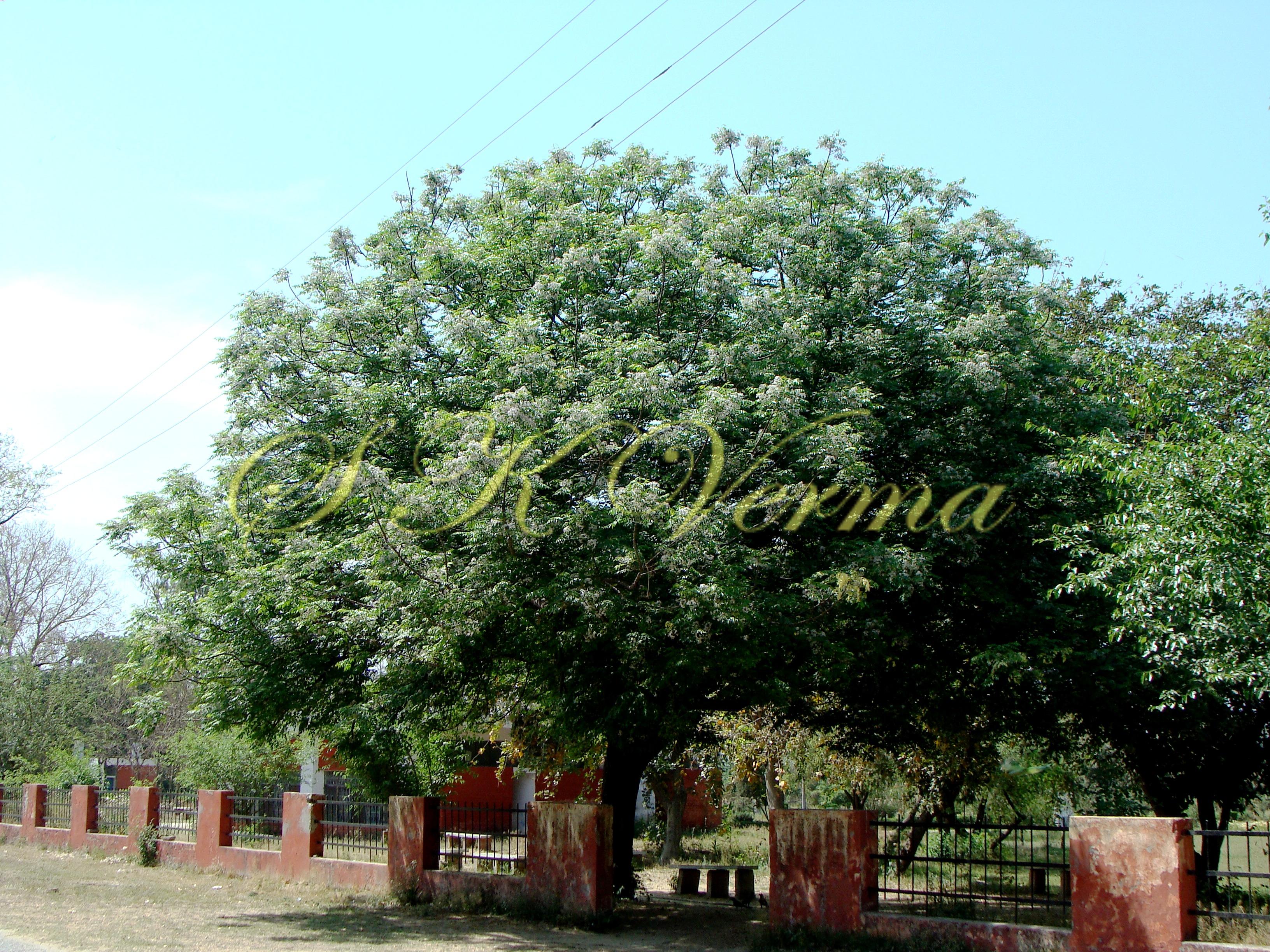
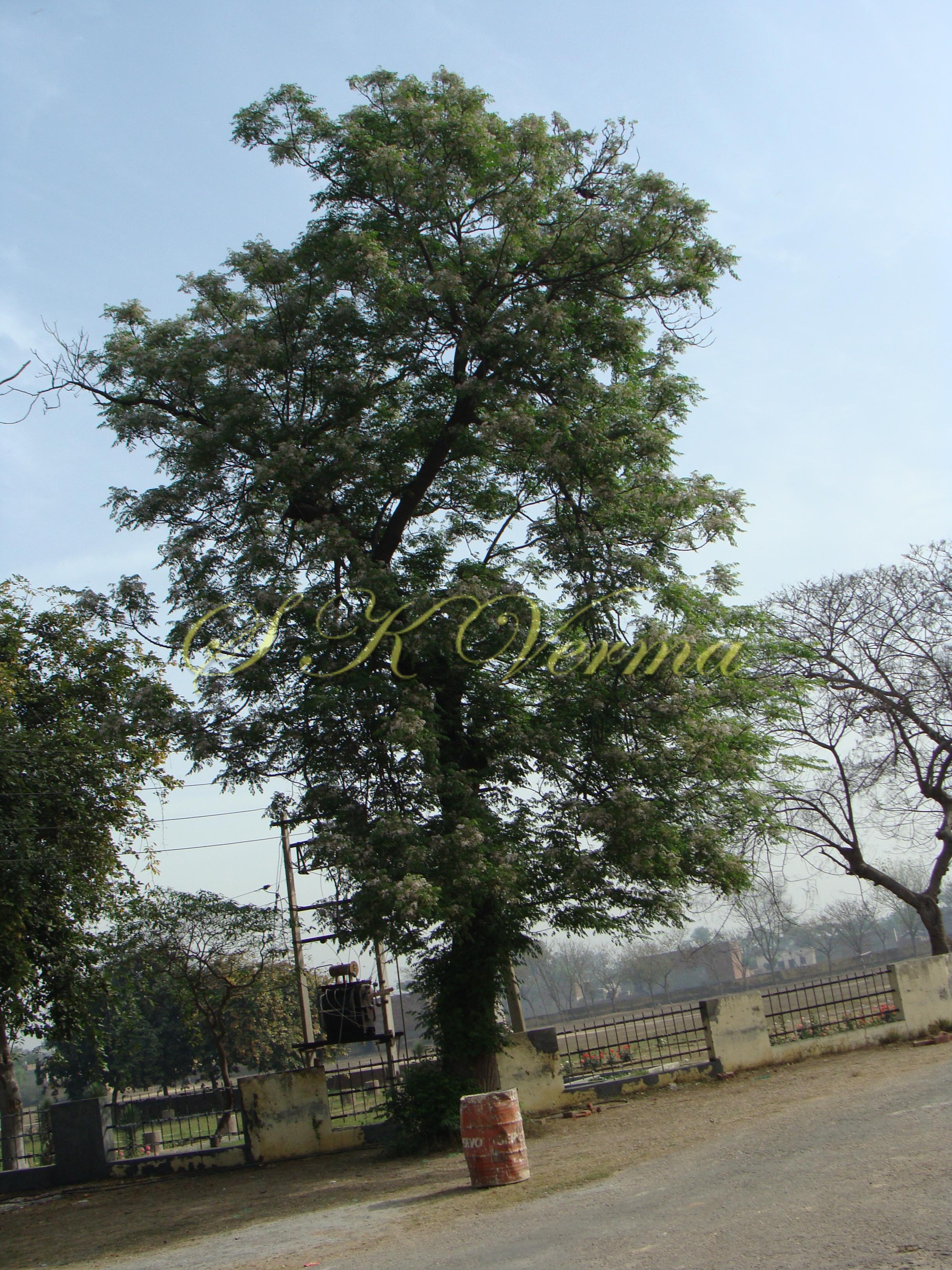
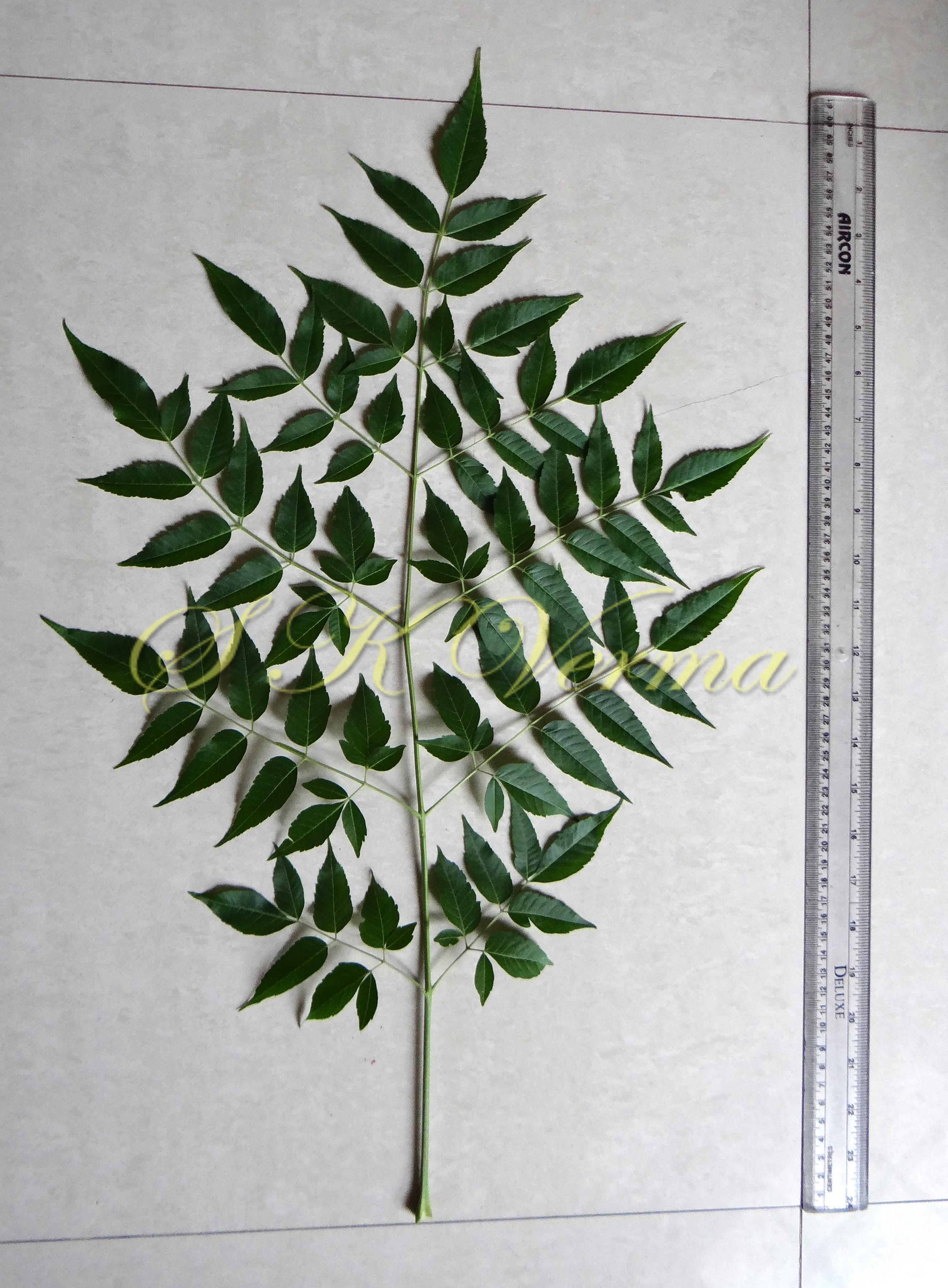
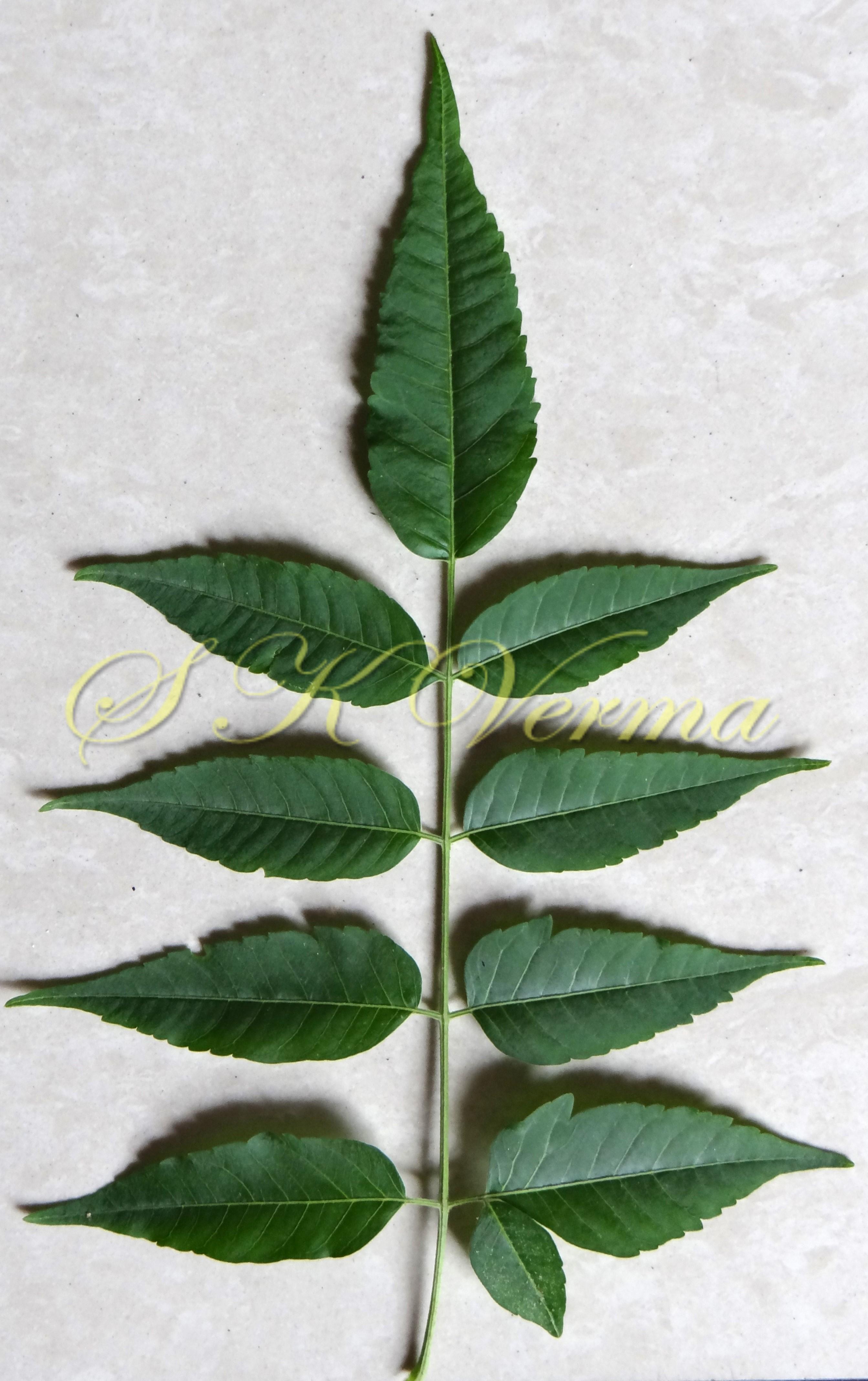
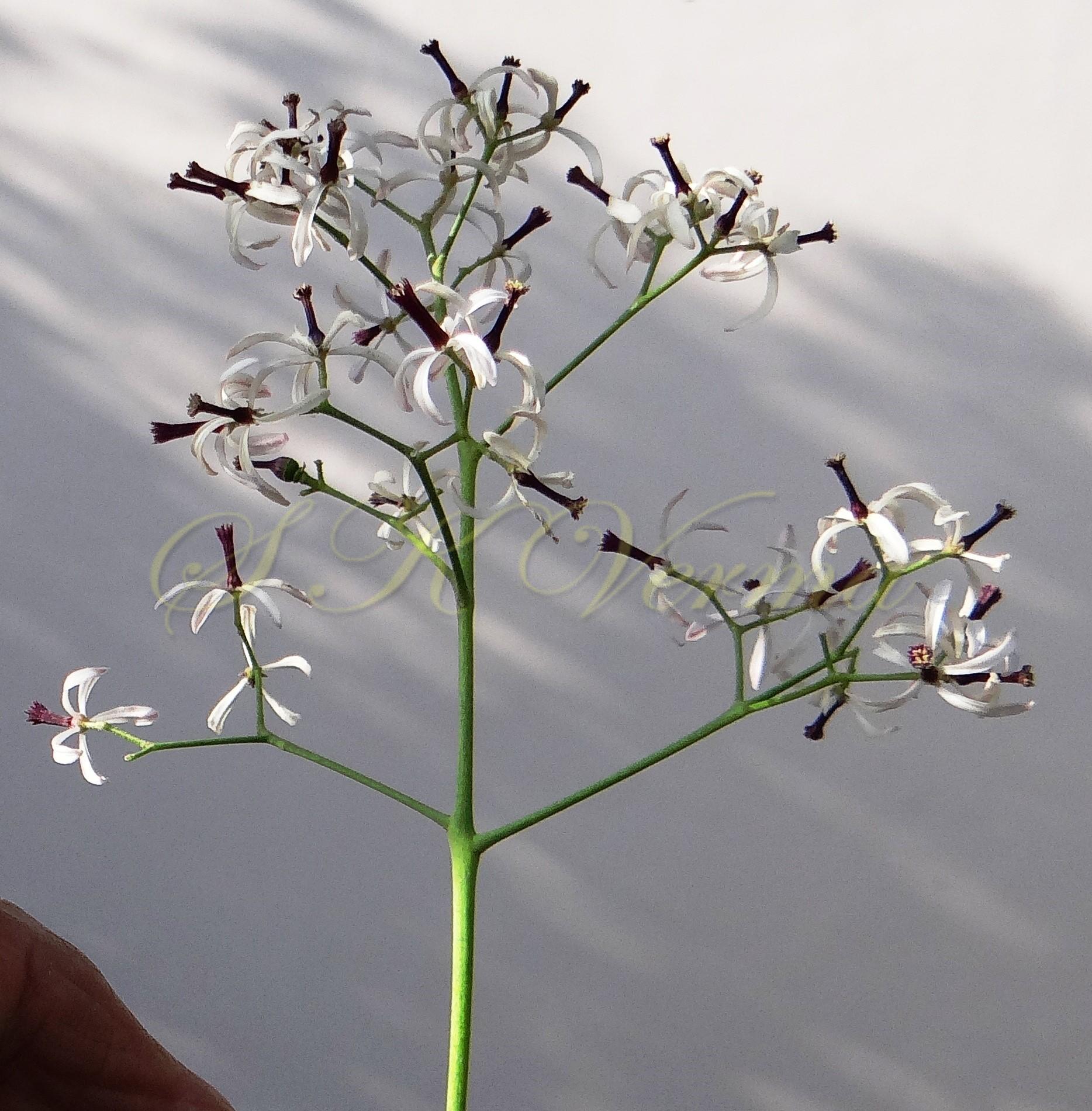
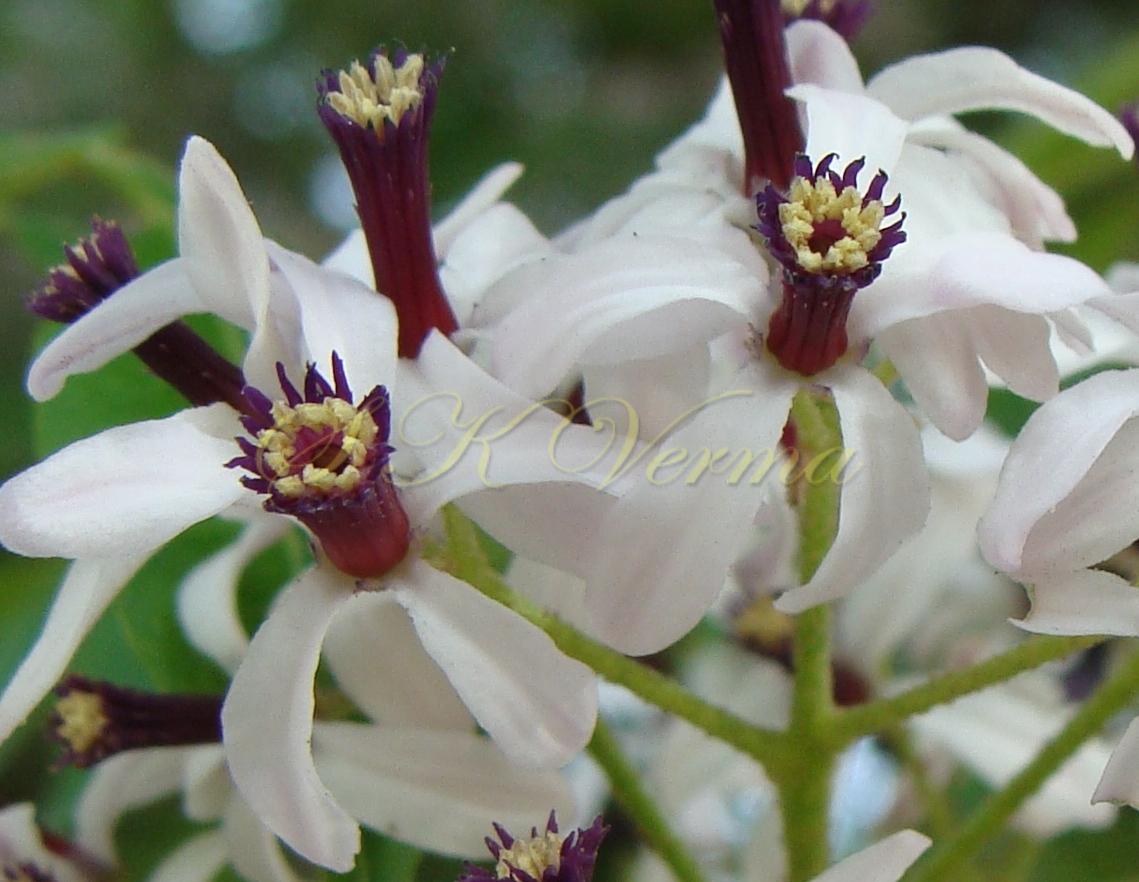
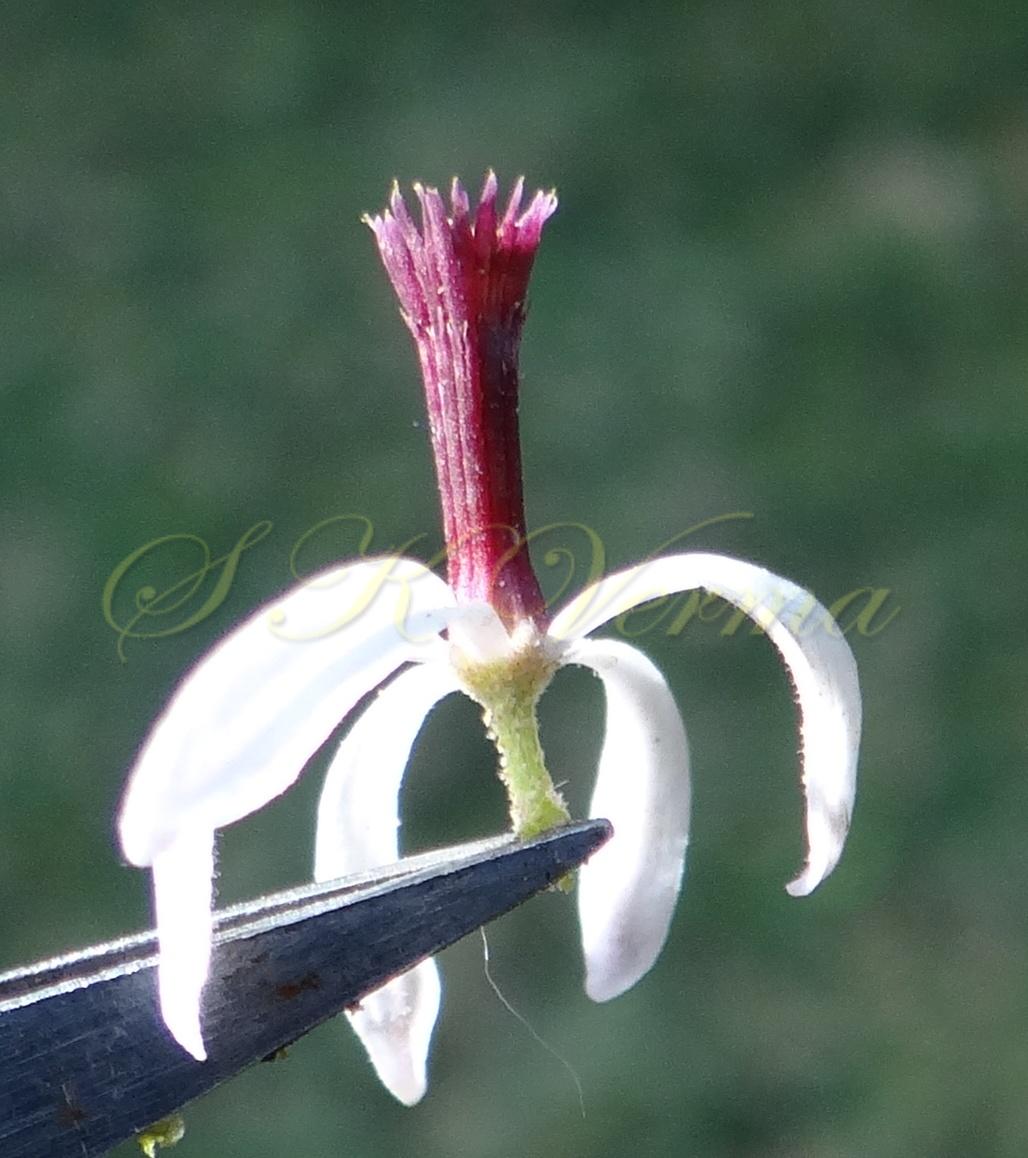
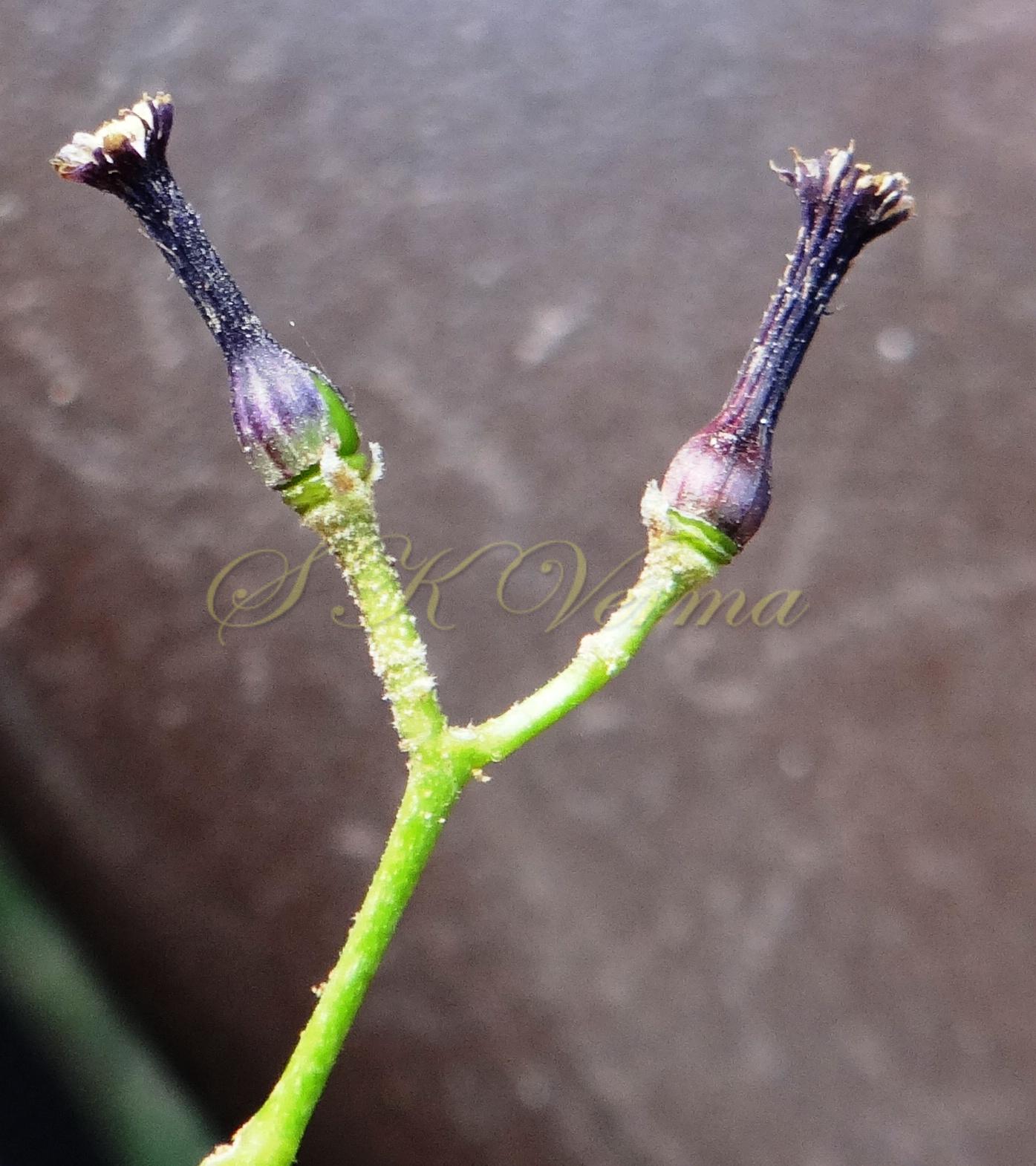
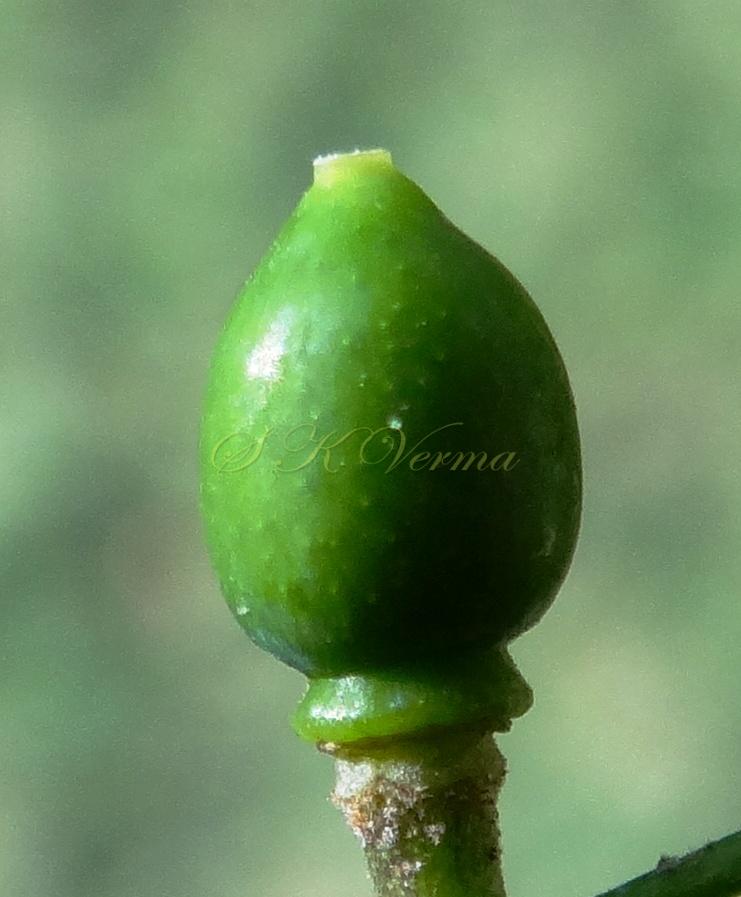
A moderate-sized deciduous tree, up to 20 m tall; bark dark grey with long shallow vertical fissures; branches spreading, branchlets with leaf scars. Leaves alternate, bi-, occasionally tripinnately compound , 24-45 cm long; petiole up to 12 cm long; pinnae 3-7 pairs, more or less opposite; leaflets 3-11, opposite or subopposite, blade 1.5-6.5 cm long, terminal leaflet larger than the laterals, ovate, obovate, ovate-obovate, oblong or lanceolate, base oblique and cuneate, margin serrate, sometimes lobed, apex acuminate, both surfaces with stellate trichomes when young, but glabrescent later; lateral nerves 6- 12(-16) pairs, parallel, slender, faint, intercostae reticulate, faint; petiolules 0-7 mm long, that of terminal leaflet sometimes longer, up to 2.5 cm; rachis, petiole and petiolules usually puberulent or tomentose. Flowers 7-8 mm long, fragrant, actinomorphic, bisexual, hypogynous, lilac-purple, in long-peduncled axillary panicles to 15 cm long, shorter than the leaves, glabrous or scurfy pubescent; pedicels short, up to 2 mm long. Calyx pubescent outside, 5-6 cleft almost to the base; lobes 1.5 mm long, ovate-oblong, acute, ciliolate. Petals 5-6, free, much exceeding the calyx, 7-9 mm x 3 mm, linear-lanceolate, both surfaces minutely pubescent, but outside more dense, lilac. Stamens 10-12, monoadelphous; staminal tube 6-7.5 mm long, dark purple, striate, puberulous, apical margin slightly dilated with 10-13 narrow lobes; lobes conic, sometimes further 2-lobed; anthers 10-12, sessile, within staminal tube at its apex, inserted between teeth, narrowly elliptic, apiculate. Disc annular. Ovary spherical, glabrous, 5-loculed, ovules 2 in each locule; style cylindric, much exceeding the ovary, ca. 4 mm long; stigma capitate. Fruit a drupe, ca. 1.5-2 cm x 1.5-2 cm, +/- globose, 5-loculed, 5-seeded or fewer by abortion, yellow and plump when ripe, becoming wrinkled and remaining on the tree long after ripening, endocarp bony with 6 longitudinal ridges, tomentose.
Common Names: Bead Tree, Indian Lilac, Persian Lilac, Pride of India, White Cedar Chinaberry, Cape Lilac, Syringa Berrytree; Bakain, Drek (Hindi)




-DSC00292.jpg)
-DSC00291.jpg)








-DSC00312.jpg)
-DSC00319A.jpg)
-DSC00314.jpg)








-DSC00292.jpg)
-DSC00291.jpg)








-DSC00312.jpg)
-DSC00319A.jpg)
-DSC00314.jpg)



